|
|
54 |
|
|
|
|
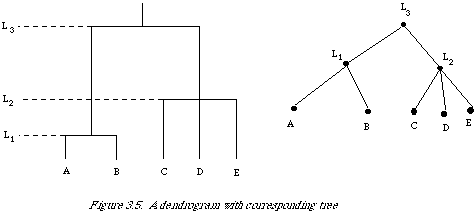
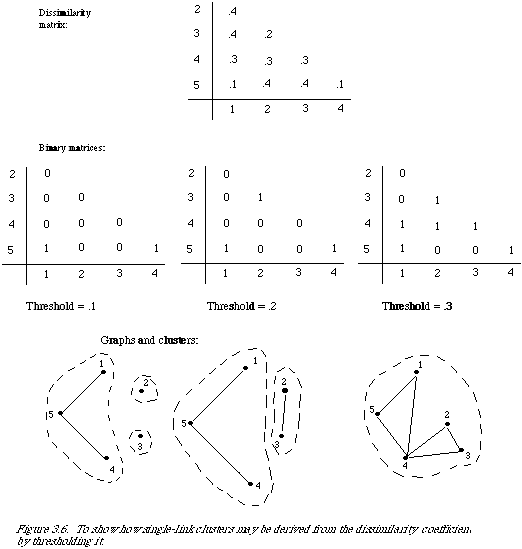
the hierarchy one can identify a set of classes, and as one moves up the hierarchy the classes at the lower levels are nested in the classes at the higher levels. A mathematical definition of a dendrogram exists, but is of little use, so will be omitted. Interested readers should consult Jardine and Sibson[2]. To give the reader a better feel for a single-link classification, there is a worked example (see Figure 3.6). A DC (dissimilarity coefficient) can be characterised by a set of graphs, one for each value taken by the DC. The different values taken by the DC in the example are L = .1, .2, .3, .4. The graph at each level is given by a set of vertices corresponding to the objects to be clustered, and any two vertices are linked if their dissimilarity is at most equal to the value of the level L. It should be clear that these graphs characterise the DC completely. Given the graphs and their interpretation a DC can be recovered, and vice versa. Graphs at values other than those taken by the DC are simply the same as at the next smallest value actually taken by the DC, for example, compare the graphs at L = .15 and L = .1.
It is now a simple matter to define single-link in terms of these graphs; at any level a single-link cluster is precisely the set of vertices of a connected component of the graph at that level.
In the diagram I have enclosed each cluster with a dotted line.
Note that whereas the graphs at any two distinct values taken by the DC will be different, this is not necessarily the case for the corresponding clusters at those levels. It may be that by increasing the level the links introduced between vertices do not change the total number of connected vertices in a component. For example, the clusters at levels .3 and .4 are the same. The hierarchy is achieved by varying the level from the lowest possible value, increasing it through successive values of the DC until all objects are contained in one cluster. The reason for the name single-link is now apparent: for an object to belong to a cluster it needs to be linked to only one other member of the cluster.
|
|
|
54 |
|
|
|