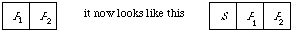|
|
81 |
|
|
|
|
(or cells) of the list structure are modified to incorporate one extra field, so that instead of each element looking like this
where the Pis are pointers and S is a symbol. Otherwise no essential change has been made to the simple representation. This structure has become known as the Doubly Chained Tree. Its properties have mainly been investigated for storing variable length keys, where each key is made up by selecting symbols from a finite (usually small) alphabet. For example, let {A,B,C} be the set of key symbols and let R1, R2, R3, R4, R5 be five records to be stored. Let us assign keys made of the 3 symbols, to the record as follows:
AAA R1 AB R2 AC R3 BB R4 BC R5
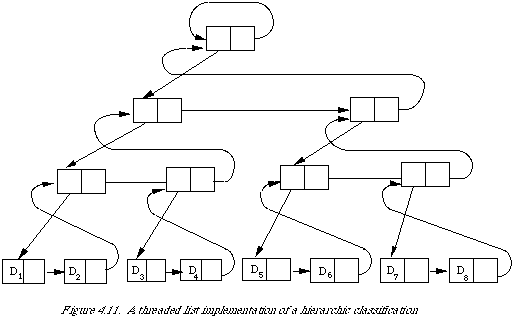
An example of a doubly chained tree containing the keys and giving |
|
|
81 |
|
|
|